To provide the best experiences, we use technologies like cookies to store and/or access device information. Consenting to these technologies will allow us to process data such as browsing behavior or unique IDs on this site. Not consenting or withdrawing consent, may adversely affect certain features and functions.
The technical storage or access is strictly necessary for the legitimate purpose of enabling the use of a specific service explicitly requested by the subscriber or user, or for the sole purpose of carrying out the transmission of a communication over an electronic communications network.
The technical storage or access is necessary for the legitimate purpose of storing preferences that are not requested by the subscriber or user.
The technical storage or access that is used exclusively for statistical purposes.
The technical storage or access that is used exclusively for anonymous statistical purposes. Without a subpoena, voluntary compliance on the part of your Internet Service Provider, or additional records from a third party, information stored or retrieved for this purpose alone cannot usually be used to identify you.
The technical storage or access is required to create user profiles to send advertising, or to track the user on a website or across several websites for similar marketing purposes.
BASIC SCIENCE II: Reproduction in Plants
Reproduction is the process by which mature individuals produce offspring. It is an essential characteristic of all living organisms.
Importance of reproduction
Modes of Reproduction in Plants
Reproduction in plants can be categorized into two types:
In higher plants, offspring are packaged in a protective seed, which can be long lived and can disperse the offspring some distance from the parents. In flowering plants (angiosperms), the seed itself is contained inside a fruit, which may protect the developing seeds and aid in their dispersal.
Plants have two kinds of parts:
Shoot – A young plant is often termed as a shoot. Generally, a shoot is regarded as a part of the plant which has stems, leaves and flowers.
Node – It is a part of the stem or branch of a plant from where the leaf arises.
Vegetative Buds – Sometimes buds are present in the leaves that are capable of developing into shoots. These are called Vegetative Buds.
Asexual reproduction in plants
1. Vegetative Propagation
As the name suggests this type of reproduction takes place with the help of the vegetative parts of the plant. Only one parent can produce the identical offspring in vegetative propagation.
Natural means of Vegetative Propagation:
Vegetative Propagation by Roots
Runners: Some plants grow along the ground and contain modified stems called Runners. These runners contain buds that can produce roots and stems. Example: Strawberries
Vegetative Propagation by Leaves
Artificial means of Vegetative Propagation
Grafting – Sometimes two plants are joined together so that both of them can provide the desired characteristics to the new plant. One plant remains rooted in the ground, which is called the Stock, and provides the essential nutrients and water while the other plants’ stem is attached to it. In this way, a new plant develops. Example: Apples
Advantages of Vegetative Propagation
2. Budding
Sometimes a chain of buds is formed which leads to the production of a large number of yeasts altogether.
3. Fragmentation
4. Spore Formation
Advantages of asexual reproduction
• Retention of useful characteristics/genes/traits
• Offspring establish faster/shorter life cycle
• Better chances of survival because of suitable environment
Disadvantages of asexual reproduction
• Lack of genetic variation
• Lowered resistance to disease
• Loss of hybrid vigor
• Competition for resources due to overcrowding
Sexual Reproduction in Plants
The flowers of a plant are its reproductive organs that participate in the sexual reproduction process.
The pistil consists of three parts:
The meaning of the following terms which describe flowers
Hermaphrodite (Bisexual)
• One with both stamen and carpel eg Hibiscus
• Most flowers are hermaphrodite/bisexual
Unisexual
Carpelate
Staminate
Dioecious plants
Monoecius plants
Complete flower
Incomplete flower
Regular flower: Those that can be divided into two similar halves by any vertical section passing through the centre. this types of flowers are radially symmetrical.
Irregular flower: Can be divided into two equal halves in one particular plane only. such flowers are bilaterrally symmetrical.
Pedicillate flower: Flower with a stalk.
Solitary flower: Those that occur singly while those that grow in cluster make an inflorescence.
Types of ovary
Superior
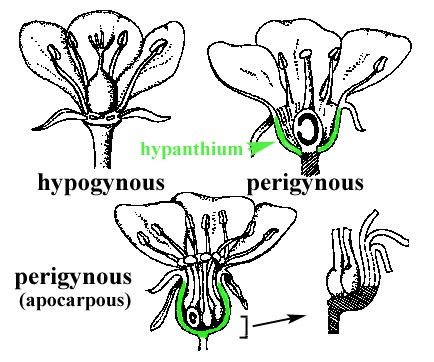
Ovary occurs above other floral parts on the receptacle.
Inferior (epigynous) ovary
Other floral parts arise above ovary on the receptacle.
How the male gametes reach the female gametes in plants.
Pollination is the movement of pollen from the stamens to the stigma, where germination and growth of the pollen tube occur. Most (approximately 96 percent) of all flowering plant species are hermaphroditic (possess both sexual functions within a plant, usually within every flower), and thus an individual can be pollinated by its own pollen or by pollen from another individual.
Types of pollination
There are two types of pollination:
There are two types of self pollination:
The Fertilization Process
How fruits and seeds are formed?
Seed dispersal
How the dispersal of seeds occurs?
You can ask our super AI Agriculture Teacher below any question of s5 and s6 agriculture and get answers